Enterprises throughout the world are rapidly starting to adopt DevOps strategies, but what does that mean? DevOps stands for Development Operations, and basically means the convergence of the Dev team, the folks creating the code, and the Operations team, those using the code. Historically, these two business units operate as silos, which has a negative impact on many factors within the organization. Some of these include slower dev times, slower time to fix security issues, and lack of collaboration between developers and users.
DevOps is really about creating a culture of collaboration and productivity by automating as much as possible, resulting in a faster time to market or more frequent releases. Enterprises that already have a DevOps mindset have a huge competitive advantage because of their ability to innovate faster, respond to business needs, and collaborate throughout the organization.
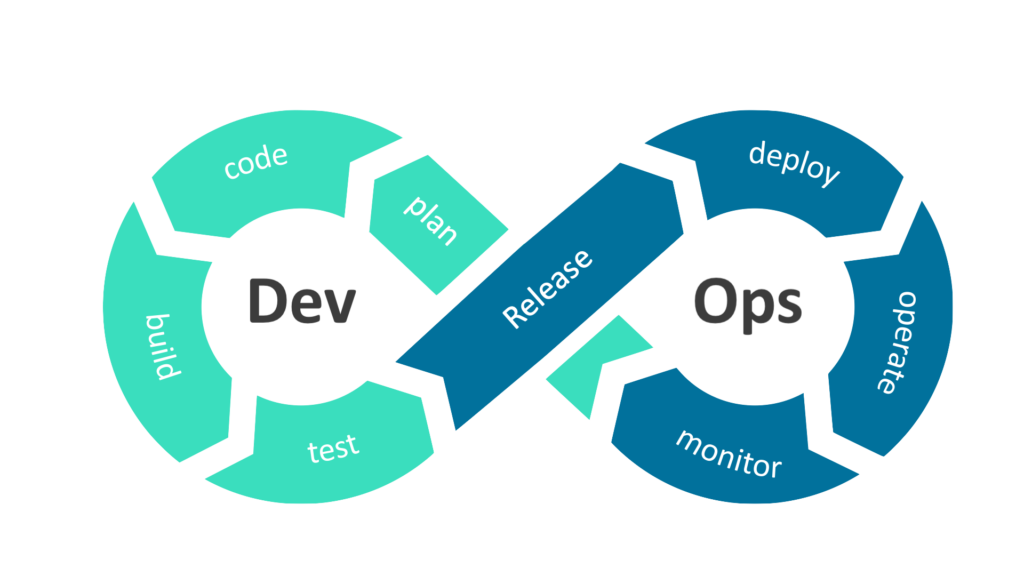
Optimal DevOps Flow Chart
There are many tools out there to help support an organization’s DevOps strategy. Below are the most commonly used DevOps management tools and a few programs within each category.
- CI/CD Management: Jenkins, Bamboo, TeamCity
- Source Code Management: GitHub, Bitbucket
- Configuration Management: Chef, Puppet, SaltStack
- Container Management: Docker, Kubernetes, Amazon ECS
- Development Environment Management: Vagrant, VirtualBox
- Code Performance Management: New Relic, Splunk
We’ll cover more of the above in future blog posts. What are some of your favorite DevOps tools?